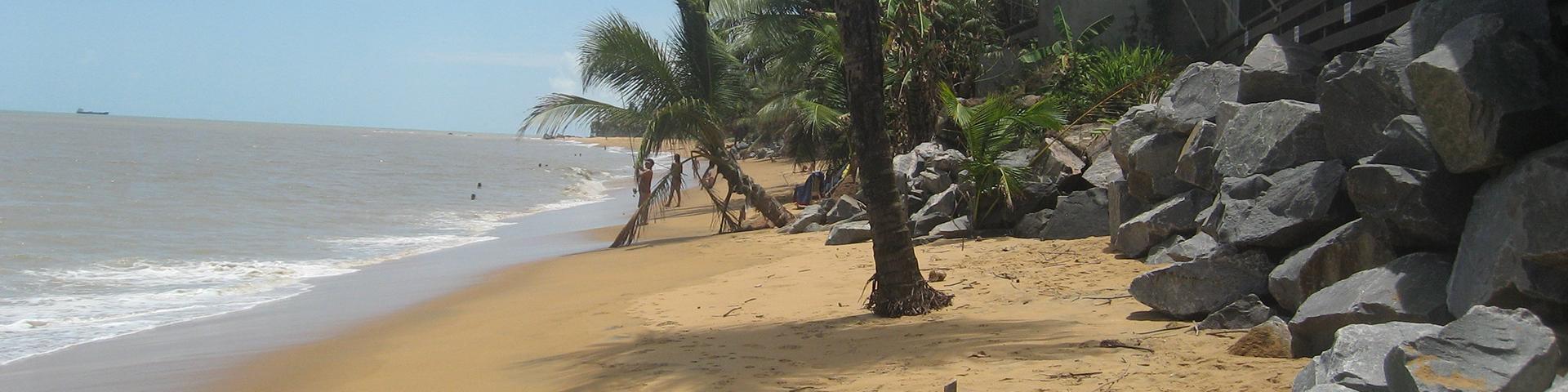
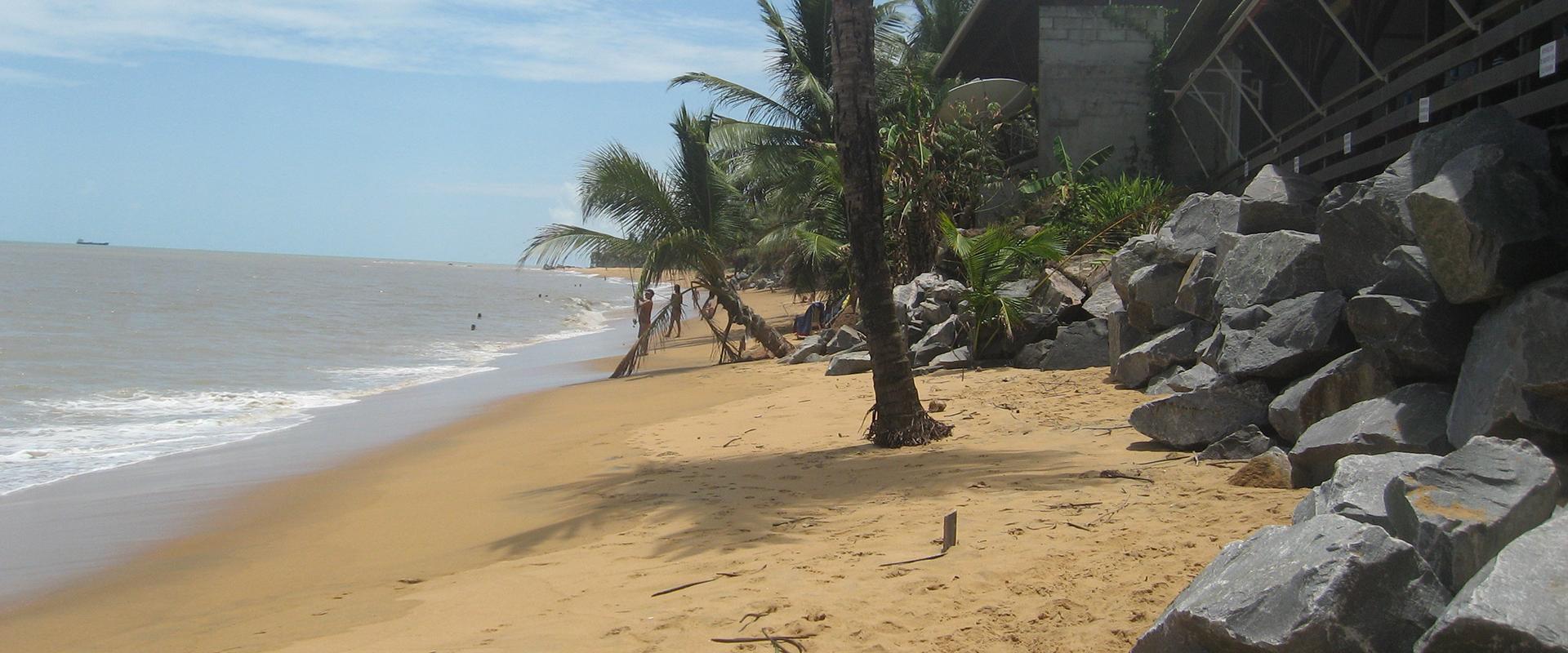
French Guiana is the only European region in South America. It has Amazonian features and covers 84,000 km², 97% of which is covered by tropical forest. The population is relatively small, estimated at just over 290,000 people, mainly located along the coastal strip and border rivers. The region's population growth is very high with an estimated annual rate of 3%, meaning the population doubles approximately every twenty years.
The economic activity consists of traditional sectors (wood, fishing, construction, public works, gold mining) and a high-tech sector, the Guiana Space Centre. The unemployment rate is extremely high (21%) and exceeds 40% among young people under 25 (half the population).
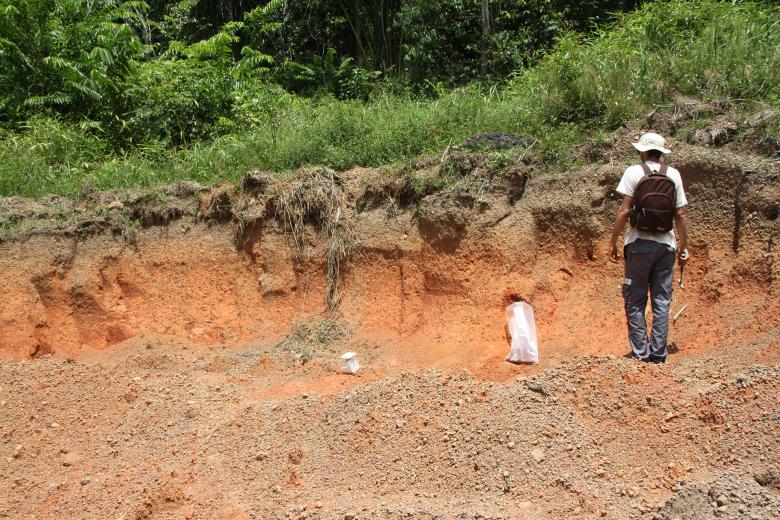
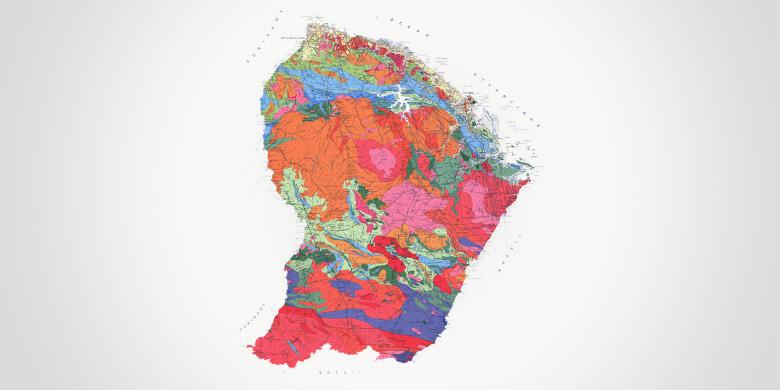
French Guiana is part of the Guiana Shield, a vast geological area bordered to the north by the Atlantic Ocean and to the south by the Amazon Basin. More than 90% of the rocks date back to the Paleoproterozoic Era, including the oldest rocks in France (2.2 billion years old). Intense chemical weathering has shaped the landscapes, with alterite formations and lateritic crusts.
Due to the contribution of erosion materials from the rivers of French Guiana and, especially sediments from the Amazon, French Guiana has one of the most constantly-changing coastlines in the world.
Partners
- Local and regional authorities: The conurbation communities (CACL, CCOG, CCEG, CCDS) and the communes (municipalities).
- Government departments and agencies: Prefecture (DGCAT, DGTM), ARS, ADEME, Conservatoire du Littoral.
- But also: Office de l’Eau, OFB, Université de la Guyane, CNRS, IRD, ONF, Météo- France, Parc Amazonien de Guyane, Grand Port Maritime and the private sector.
Practical information
To find out more
What's new in French Guiana?
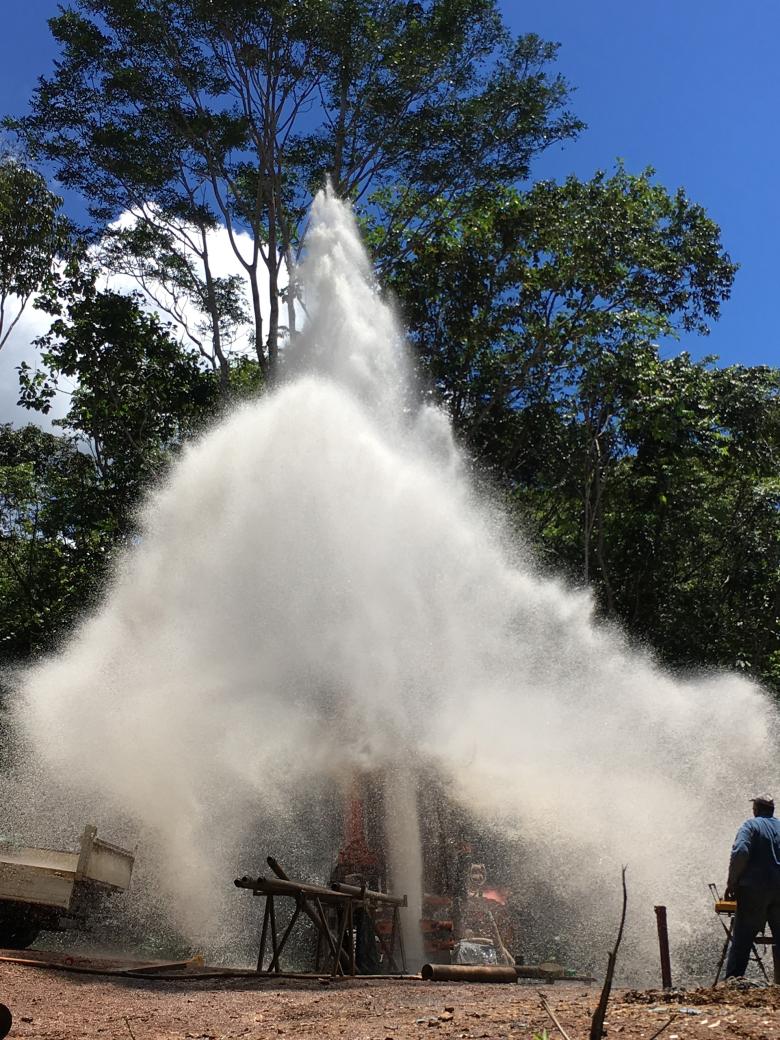
Groundwater management: exploiting and protecting groundwater
With more than 112,000 km of waterways, French Guiana has abundant water available per capita; however, this resource is unevenly distributed, with 46,000 inhabitants currently not having direct access to drinking water.
A total of 75% of the drinking water supply comes from rivers (compared to 25% from groundwater sources) but this percentage is gradually decreasing. BRGM monitors the piezometric levels and chemical state of groundwater bodies in the French Guiana basin, develops hydrogeological prospecting programmes and assists local stakeholders in drilling. It also develops projects to model saline intrusion in coastal rivers, monitors river turbidity and assesses pollution of agricultural origin (particularly pesticides) and from trace metals.
Risks and spatial planning: forestalling hazards
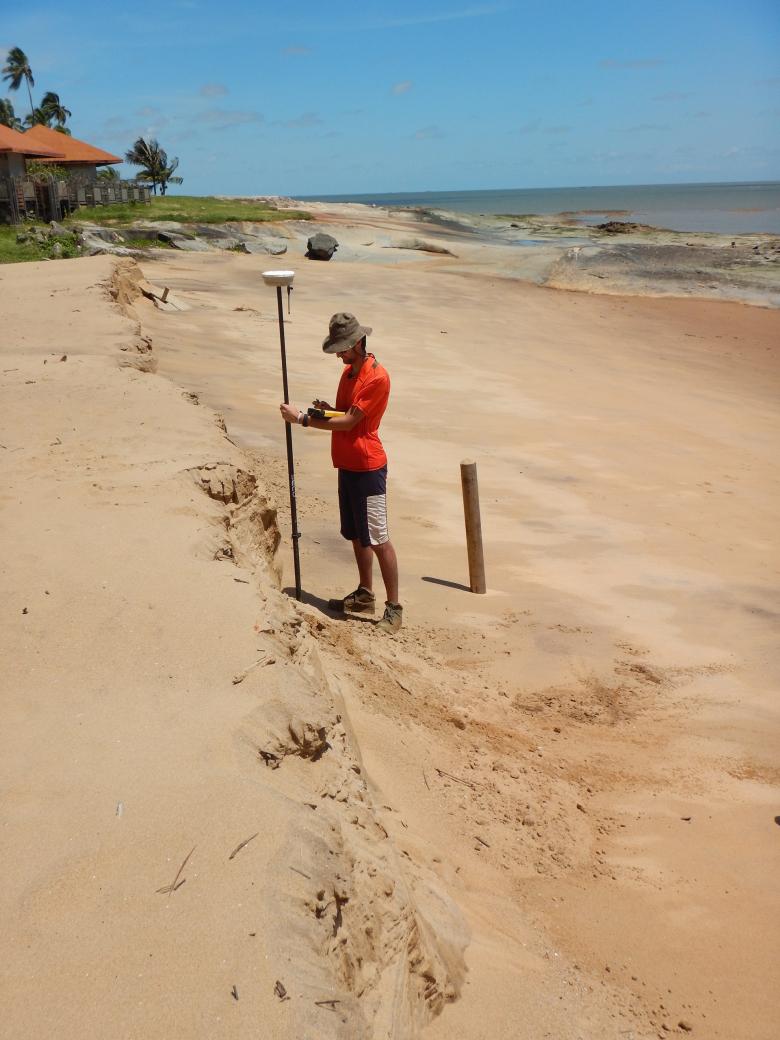
Areas on the island of Cayenne and in Kourou with steep slopes that are subject to land movement due to heavy rainfall and urban development, among other things. Subjected to north-east swells, the shifting of Amazonian mud banks and rising sea levels, the coastline is vulnerable to coastal flooding and erosion.
In conjunction with the French Guiana DEAL, BRGM has been co-managing the Observatory of Coastal Dynamics of French Guiana (ODyC), a tool for acquiring data on coastal dynamics, and for providing input for public coastal management policies.
BRGM helps draw up risk prevention documents (PPR, Hazard maps, awareness-raising brochures, etc.) and is involved in crisis management activities. BRGM works with some communes that are particularly affected by coastal flooding and erosion episodes, in order to develop a management strategy for the coastline.
Mineral resources and the circular economy: improving the resilience of regions to climate change
The establishment of a comprehensive set of data is essential for research work as well as for applications linked to mineral resources (mines and quarries). The need for construction materials (sand, rock, laterites, clays), to respond to the strong demographic growth in French Guiana, is another major challenge.
BRGM is helping the government and the mining industry to improve methods for characterising and exploiting deposits (particularly gold deposits) through good prospecting practices and efficient mining techniques aimed at reducing environmental impact. It provides its expertise to help locate deposits of construction materials (sand, rocks, laterites) and to promote the green economy (clay deposits for manufacturing mud bricks). It is also developing methodologies for assessing the recycling potential of secondary materials to promote the circular economy.
And also:
- Analytical traceability of gold through the EU TAO project and support for sustainable mining,
- Support for managing sand extraction in the Maroni River,
- Updating of the “Regional Quarry Plan”.
Geology and knowledge of the subsurface: the development of geothermal energy and risk management
Improving geological knowledge is a major priority for BRGM, and concerns several sectors.
BRGM contributes to improving geological knowledge and helps pass on this knowledge to its partners and the general public, particularly through its involvement with the University of French Guiana as part of the VALORESS vocational degree course and the publication of the Guide to the Geological Curiosities of French Guiana. It has also made data about mineral resource assets publicly available by archiving mining inventory data and setting up a carothèque (core samples database). It also participates in several actions:
- The project for a helicopter-borne geophysical campaign (“EMCAY”) on the island of Cayenne, will identify areas that are potentially vulnerable to ground movements (3D TDEM model);
- Prospecting for rock and mineral deposits;
- Identification of hydrogeological potential;
- GEOSOL project: updating of geological maps of French Guiana for the Regional Authority of French Guiana.