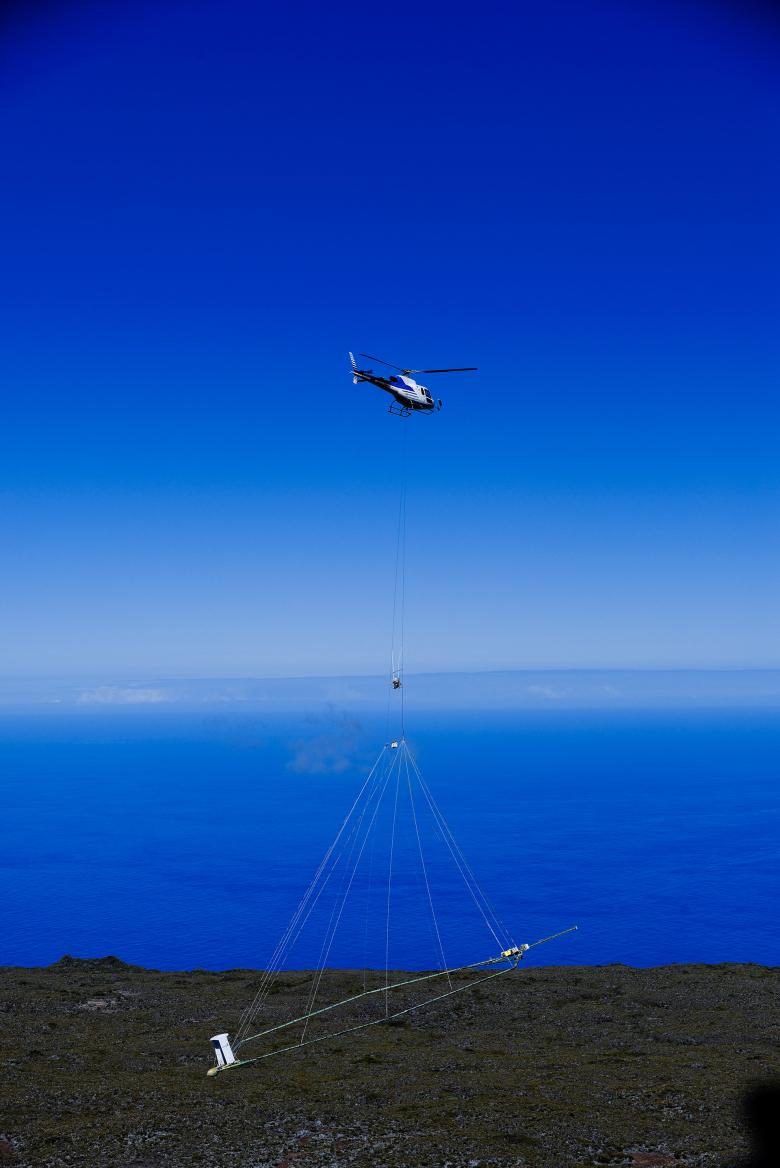
As of 3 March 2022, the Danish geophysics company SkyTEM will be chartering a helicopter from Tahiti Nui (a local helicopter rental company) in order to conduct a four-to-five-week survey over part of French Polynesia, according to a flight plan drawn up by BRGM covering almost 1000 km. Flying at a height of between 50 and 80 metres, the helicopter will carry a 25-metre-diameter antenna, designed for remote sensing of the Polynesian subsurface.
Improving knowledge about the subsurface structure and gathering valuable data for various regional entities and organisations
The survey campaign has a dual objective. In the short term, the data gathered will help improve local hydrogeological knowledge, with the ultimate aim being to extend the drinking water supply system on the islands surveyed. Overall, BRGM will probe the subsurface of 4 Polynesian islands, representing a total area of 881 km2. Then, in the medium term, the data gathered will be used to set up a reference geophysical database for the islands concerned. In the future, this database could be exploited for various applications, along the lines of similar surveys carried out in the French Overseas Territories and in mainland France.
The project was initiated and financed by the municipalities of Moorea-Maiao and Bora Bora, the Syndicat pour la Promotion des Communes de Polynésie Française (on behalf of the municipality of Tahaa, which shares responsibility for the management of drinking water), with the support of French Polynesia, the French State and BRGM. It will enable the municipalities concerned to have a better understanding of their area's geology and thereby optimise the use of their groundwater resources. The main goals are to improve knowledge about the water tables in order to ensure their sustainable management and to establish protective perimeters with regards to catchment areas and boreholes.
Specific local issues
Each local area has its own specific issues. On the island of Maiao, there is currently no public-service water supply (private, individual systems only). Then, on Moorea, the water supply service is frequently under pressure, notably during peak tourist periods, but also due to seasonal variations in resources.
The main objectives on Bora Bora are to increase the share of groundwater in the drinking water supply (currently 50%) and to better define the protective perimeters for the freshwater aquifers, particularly on Motu Tevairoa. The overall aim is to support and facilitate urban development.
As regards Tahaa, the municipality has been experiencing water shortages for several years, particularly in the south of the island. So, in this case, the key objective is to identify new groundwater resources.
Simultaneous use of two geophysical methods
To carry out these heliborne surveys, two geophysical methods will be used at the same time.
Electromagnetic scans will be used to show electrical resistivity contrasts across the first 250 to 400 metres of the subsurface. These contrasts will provide information about the nature, porosity and weathering of the rocks, in relation to the hydrogeological characteristics of the geological formations.
Magnetic scans will map the magnetic field to a depth of more than a kilometre below the surface, providing information about the islands' volcanic and tectonic structures, which may influence groundwater flow.
Further information
Press contact