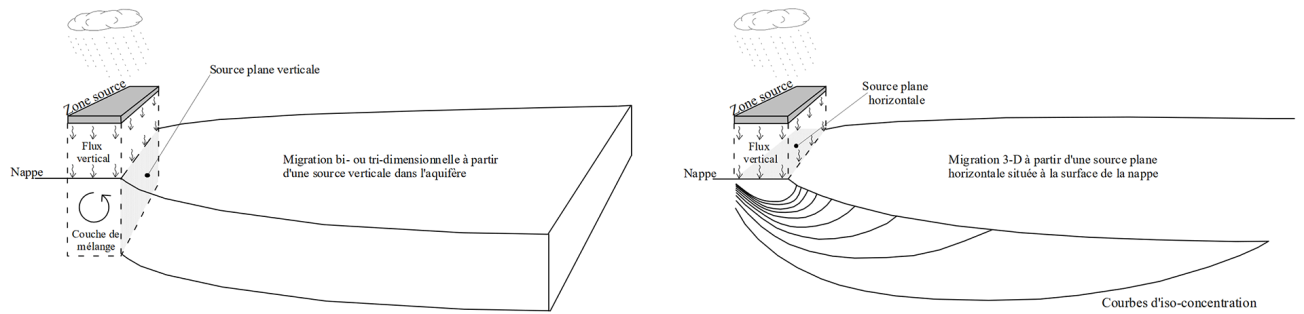
Left: Conceptual model of some analytical tools used to estimate the impact of contaminants on groundwater. Right: the MISP conceptual model.
© BRGM
MISP was developed to tackle the problem of pollution from sources located above the water table. This is relevant in a number of situations, such as when waste is buried near the surface or when superficial soils are contaminated. Pollutants are washed downwards by meteoric water infiltrating the ground, and then transported to groundwater bodies. Once they reach these, they move sideways with groundwater flows, and go through a number of attenuation processes. The main feature of MISP compared to similar available tools is that the model does not rely on the “mixing layer” hypothesis to calculate pollutant concentrations in groundwater directly below a pollution source.
This approach is problematic because it relies on a homogeneous and instantaneous mixing layer, which in reality is never found in groundwater. Mixing is a gradual process resulting from several phenomena, including spatial variation of the velocity field, lateral dispersion and density effects.
Using a convolution approach, the MISP model combines an analytical solution for vertical migration through the layer directly above the aquifer and the solution proposed by Galya (1987), which considers tri-dimensional migration from a plane source on the water table. Galya used Green’s functions to develop a solution for modelling the tri-dimensional migration of solutes from a constant-flux horizontal plane source located on the water table. The concept behind MISP was to use the convolution principle to combine this solution with a solution for modelling vertical migration from a source located above the water table.
The following are examples of concentration calculations that have been derived from the processing of MISP results:
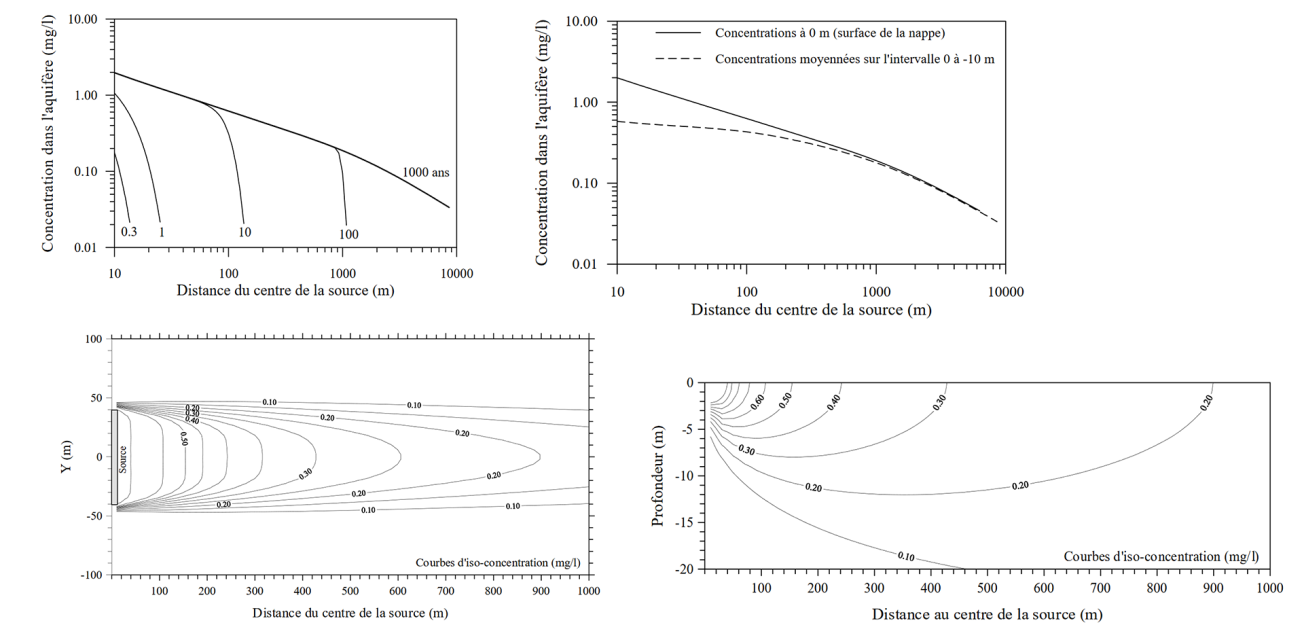
A few examples of concentration calculations derived from the processing of MISP results.
© BRGM