Your challenges and needs
Would you like to model flows and transfers in aquifer systems in 2D or 3D, integrating climatic influences, anthropogenic influences and possible geochemical reactions, in different contexts?
BRGM has developed the MARTHE (Modelling Aquifers with a Rectangular Mesh, Transport and Hydrodynamics) software package, which enables 3D modelling of flows and mass and energy transfers in hydrosystems. The modelling incorporates aquifers, watercourses and the unsaturated zone.
Our added value
MARTHE is an application for computing pollutant and energy flows and transport in porous environments (in aquifers) developed at the BRGM. This application, based on the finite volumes method, is a complete code incorporating:
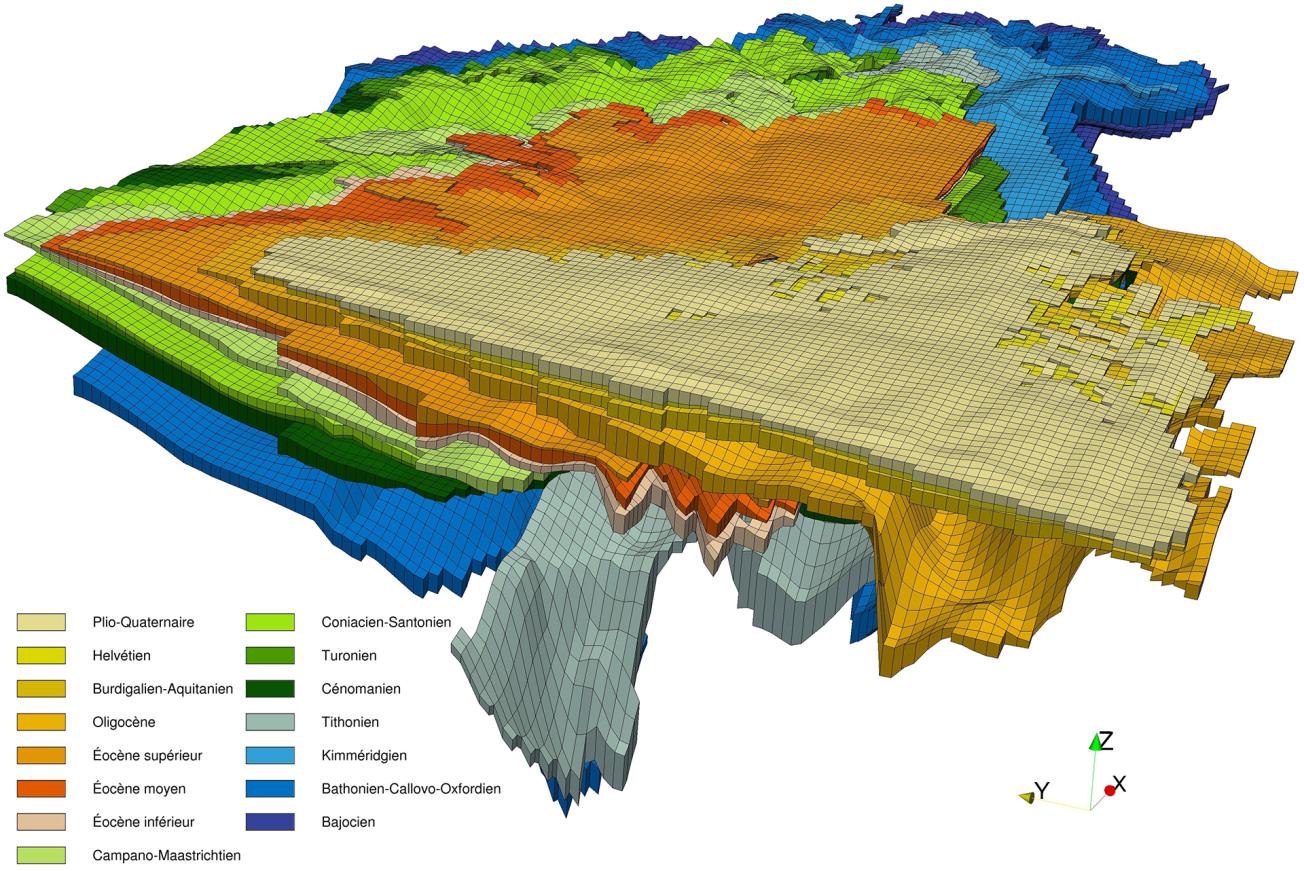
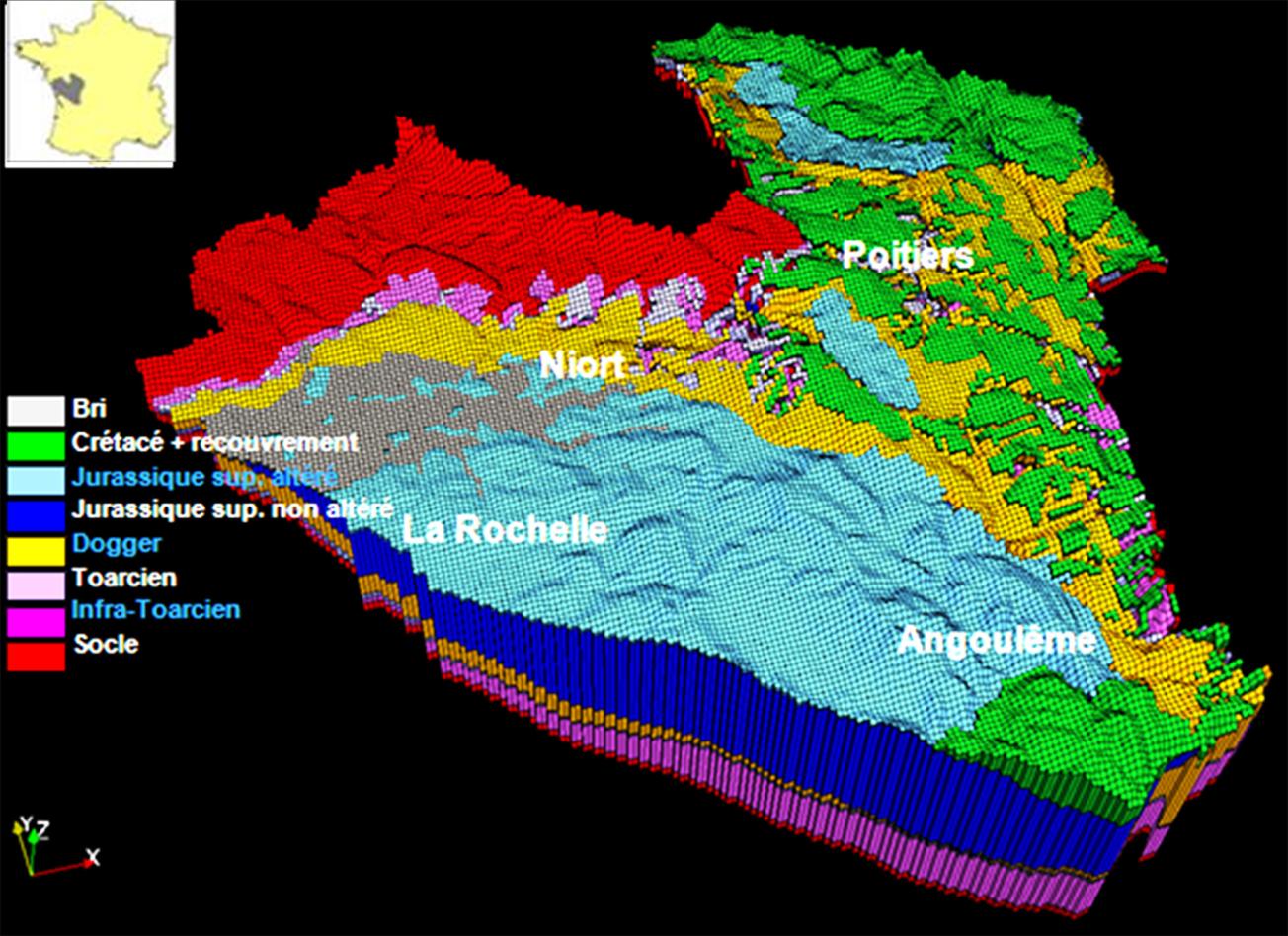
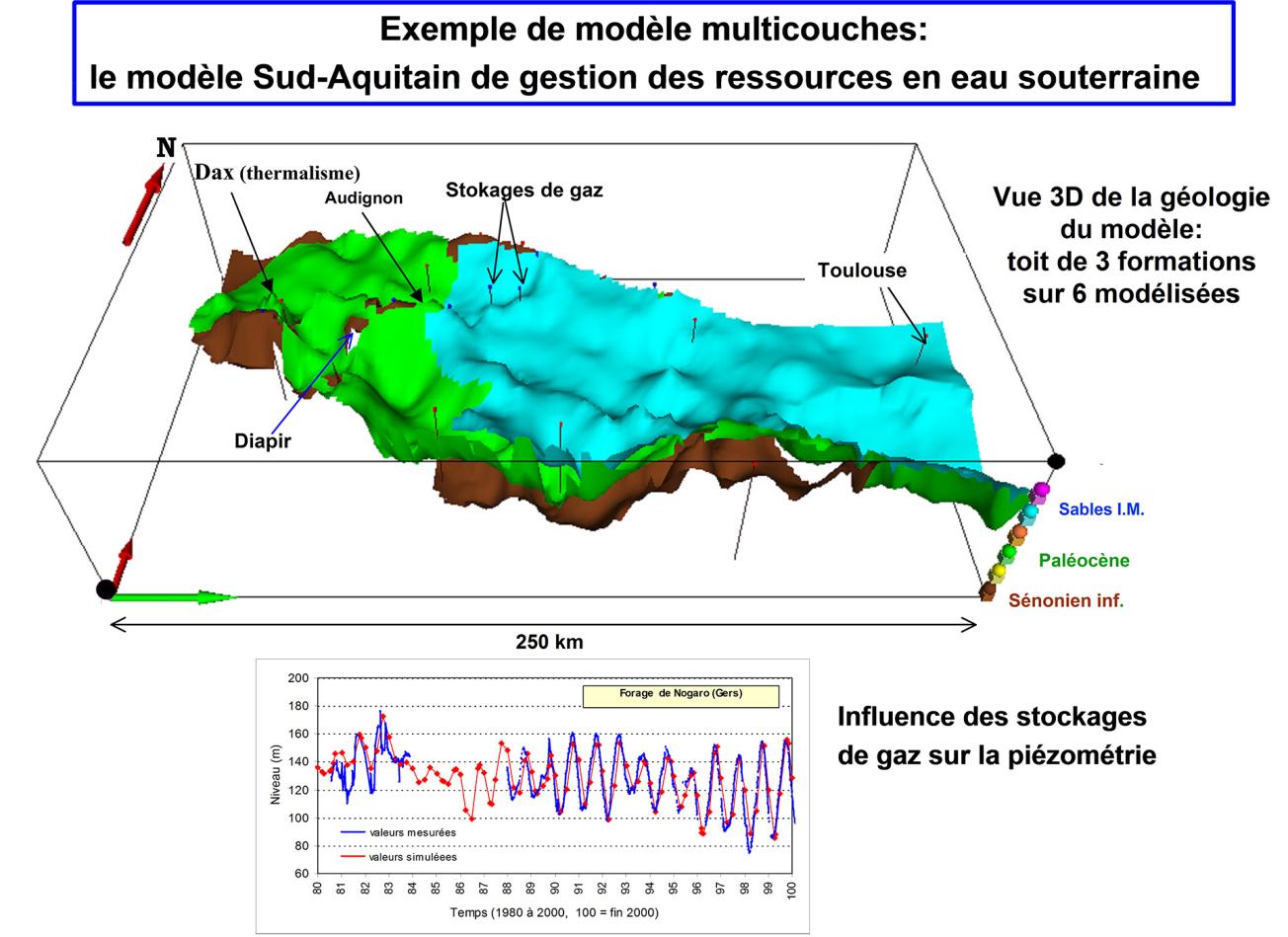
- single-layer and multi-layer aquifers and 3D,
- hydrographic networks (rivers, other waterways, drainage),
- exchanges with the atmosphere (rain, snow, evapotranspiration).
The calculations may also include:
- mass transfer, for water quality protection,
- temperature effects,
- influence of salinity,
- degradation of pollutants,
- transfers through the vadose zone,
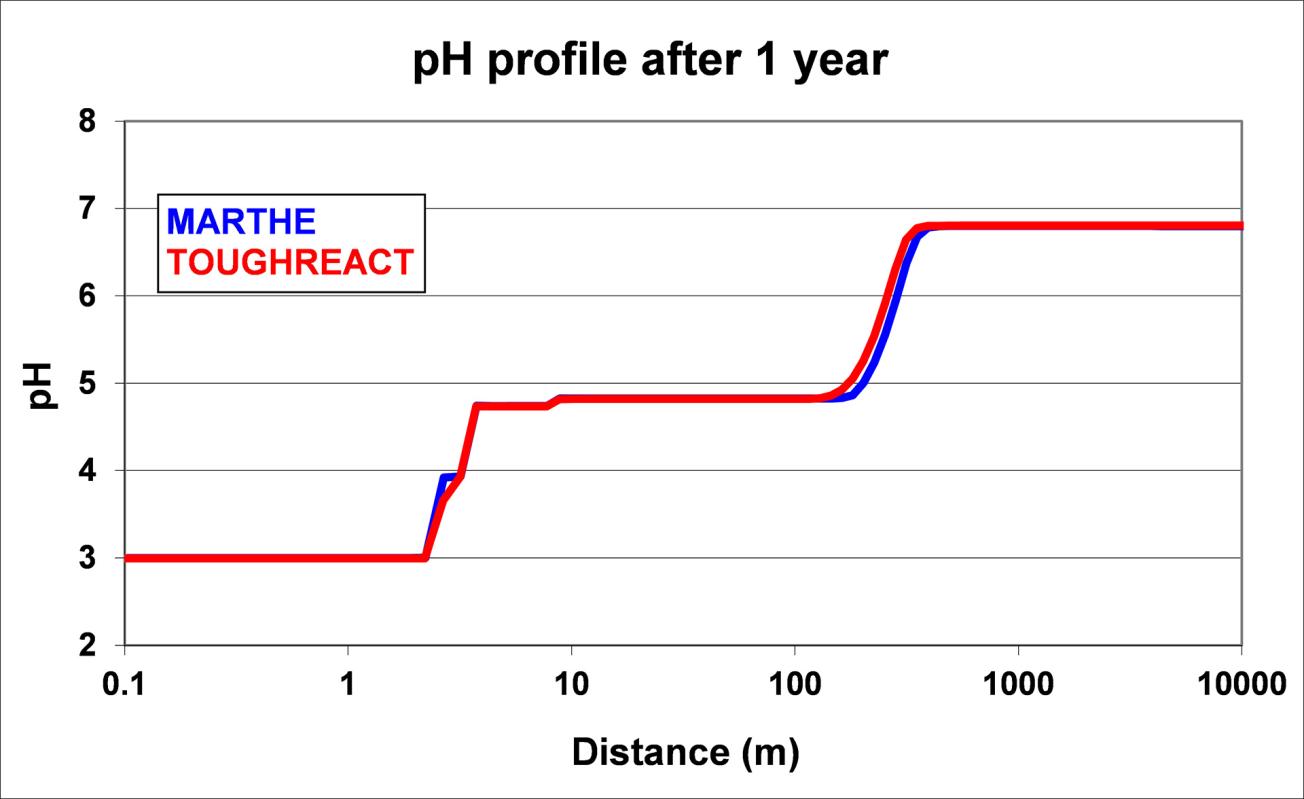
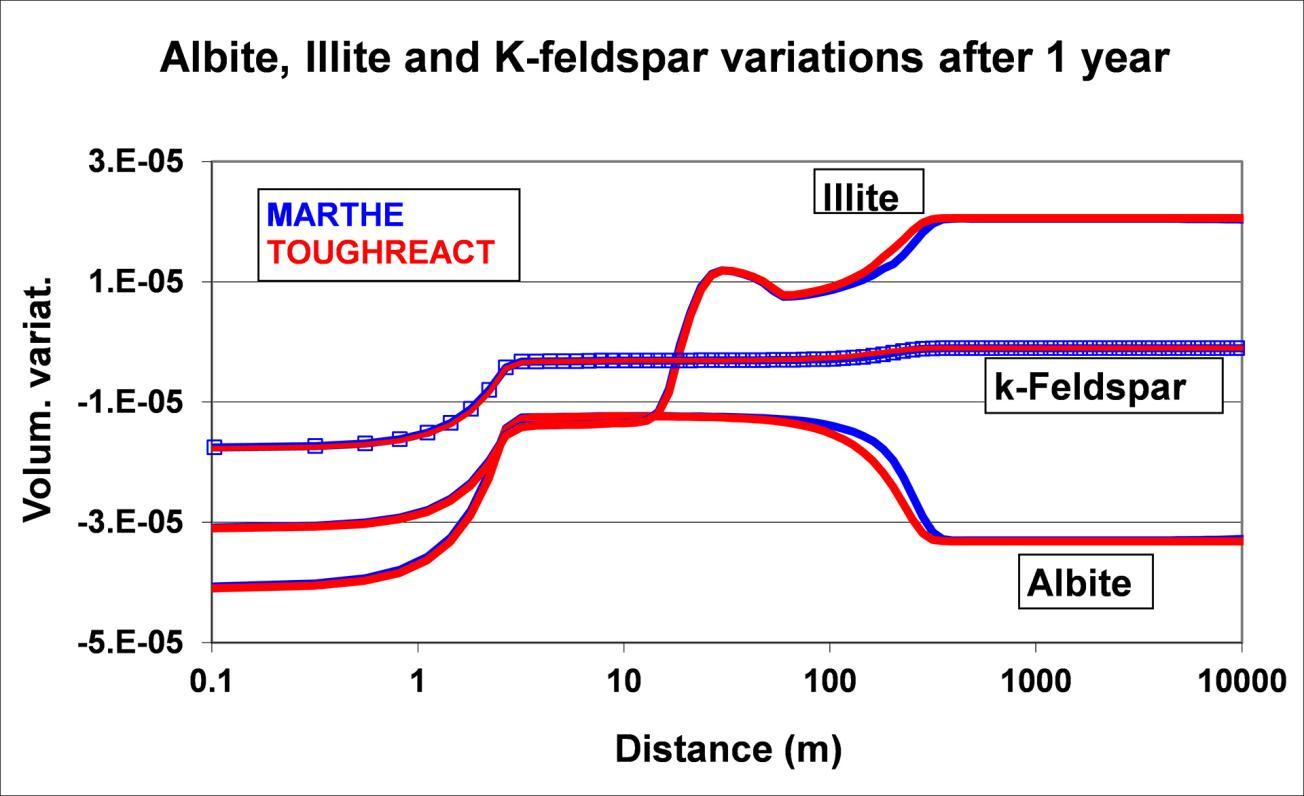
- geochemical interactions with Phreeqc or React modules.
MARTHE: Modelling software for groundwater flows
MARTHE: areas of application
MARTHE is designed to model fluid flow and transfer issues in different contexts:
Management of aquifer resources
- Assessment of water budget components in an aquifer system: rainwater recharge, lateral input from catchment areas, underground circulation and associated flows, year-on-year fluctuations, seasonal storage and release,
- Hydrodynamic impacts of existing or planned structures: pumping, irrigation, drainage, gravel beds, retention basins,
- management and optimisation of catchments,
- studies of the influence of climate variability and predicted climate change impacts,
- diagnoses of groundwater pollution,
Environment
- Pollutant infiltration into the vadose zone, percolation to the aquifer followed by groundwater migration,
- simulation of a pollution plume released from a contaminated zone: pathlines, velocities, downstream concentrations.Modelling hydraulic scenarios for confinement or decontamination,
- impacts of domestic and industrial landfill on groundwaters,
- studies of underground storage confinement.
Civil engineering and mining
- dewatering of excavations
- hydraulic effects of impermeable walls,
- below-ground worksites (underground, car parks, tunnels),
- calculation of mine dewatering and corresponding drawdown.
Learn how to use MARTHE
BRGM Formation is offering a course entitled “Hydrodynamic modelling with the MARTHE software (© BRGM)”.
This course, which is intended for engineers needing to model the behaviour of aquifer systems so as to manage water resources or undertake pollution studies, can be delivered within companies, in France and abroad.
The advantages of the course
The MARTHE software (Modélisation d'Aquifères avec un maillage Rectangulaire, Transport et Hydrodynamique [Aquifer modelling with rectangular grid cells, for studying transport and hydrodynamics]) is used for 3D modelling of mass and energy transfers in hydrosystems. The modelling includes aquifers, water courses and unsaturated areas.
To find out more

MARTHE functions
General functions
- 1D, 2D or 3D ("full 3D") grids.
- Calculations by finite volumes on structured grids with possibilities for nested grids.
- Single or multilayer aquifers (layered aquifers, sometimes separated by a semi-permeable aquitard).
- Unconfined, confined or semi-confined aquifers in steady or non-steady state.
- Calculations may include discontinuities such as open water bodies (lakes, gravel pits), local aquifer depletion (and subsequent recharge), including in multilayer aquifers, groundwater flooding (rivers, springs, drains), impermeable walls (sheet pile walls, etc.).
- Automatic limitation of pumping rates as pump heads are uncovered.
- Calculation of well hydraulic head according to well diameter compared to the size of the grid cell containing it.
- Full coupling with hydrographic systems (rivers, drains).
- Coupled hydro-climatic calculations for rain, evapotranspiration, infiltration and runoff: the GARDENIA computing procedure.
- Horizontal and vertical anisotropism of permeable areas.
- Calculation of (direct and reverse) pathlines in steady or non-steady state.
Grids
- The field corresponding to each layer to be modelled is discretised into a structured rectangular tartan grid.
- The width of each line and column may differ with local heterogeneity, the density of available information and the level of accuracy required.
- The grid can be further refined locally with nested sub-grids.
- Grids can be in vertical cross-sections or radial (cylindrical coordinates).
- Several million cells can be handled, the maximum cell number depends purely on the physical memory installed.
- Maximum potential capacity:
- 3000 columns, 3000 rows, 999 layers, 99 nested layers.
- Unlimited calculation time steps.
Hydrodispersive transport
- Hydrodispersive migration of an effuent in the aquifer and the vardose zone.
- Calculations use the TVD method ("Total Variation Diminishing"), the MOC method (Method of Characteristics) or the Finite Differences method.
- Chain-reaction degradation
- Retardation factor, kd partition coefficient (adsorption-desorption)
- Sorption by Langmuir or Freundlich isotherm.
- Possibilities for control of injection well concentration by production well concentration,
- Reactive transport with PHREEQC (USGS) geochemical modules.
Non Saturated Zone, Density effects, Temperature
- Continuous flow and transfer in the saturated zone and the vadose zone.
- Energy transfers, water temperature calculations.
- Density effects due to variations in salinity and/or water temperatures.
- Influence of temperature on viscosity and degradation coefficient taken into account.
- Possibility for control of injection well temperature by production well temperature (geothermal doublets).
Automatic calibration, sensitivity analyses
- Automatic calibration of model parameters, defined per homogeneous zone or per grid cell.
- Sensitivity analysis to the calibrated parameters.
Specific applications
- Vertical fracturing simulated by equivalent transmissivity.
- Semi-pervious vertical or horizontal fractures
- Gallery networks taken into account.
- Diphase flows with non-miscible phases: freshwater and salt water, water and air, water and "oil".
- Gas flows.
- Vegetation growth taken into account.
- Nitrate or nitrogen balance resulting from crops.
Visualisation, import and export
- Pre-processor and post-processor through graphic interface
- Detailed "help" file
- Input interface with 3D modellers:Multilayer ®, GDM ®, EarthVision ®, Éclipse ®, Surfer ®.
- Export to Mapinfo ®, Paraview, Tecplot ®, Winteracter-3Dview ®, Vrml QGis, ArcGis ® for 3D displays.
- Export to Mapinfo ®, QGis, ArcGis ®, Surfer ® for 2D displays.
- Export to Microsoft Excel ® to display series.
Calculations in non-steady state
Any grid-cell information can be modified at each calculation time step:
- hydraulic head, temperature, concentration, salinity,
- pumping and injection flow rates, rainfall, potential evapotranspiration, air temperature, recharge,
- permeability, porosity, riverbank clogging, extent of hydrographic network or drains,
- topographic elevation,
- setting or release of prescribed hydraulic heads,
- etc.

Downloadable documentation
Note: Dialog box, inputs and outputs of the software are in English; however the documentation and help files are in French, with the exception of the English version of the tutorial.
Publications on studies conducted with MARTHE software