ViSéGéo: the integrated "geotechnical drought watch" solution
The need
Given that it is the second largest Cat Nat (natural disaster) compensation item after floods (more than €2 billion in 2022 according to CCR) and that climate change is likely to increase the frequency of "drought" crises, strategies for managing the risk of clay shrinkage and swelling are based on prevention and adaptation measures for new buildings and involve:
- hazard mapping, carried out on the scale of individual French départements, which characterises areas that are potentially subject to such phenomena, without taking into account the drought phenomenon itself, which is the triggering factor for them,
- drawing-up of a "Drought" Risk Prevention Plan (PPR - Plan de Prévention des Risques) at the local level at the instigation of the Prefectures concerned,
- compliance with simple measures when constructing buildings on ground that is subject to RGA, etc.
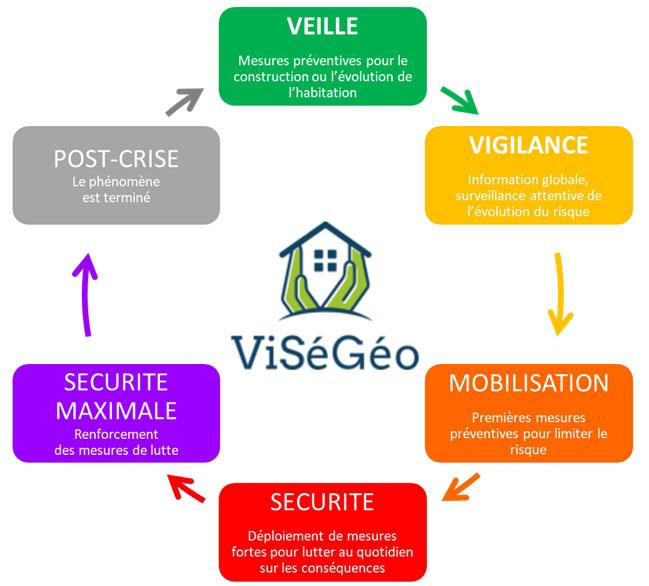
No strategy is currently being developed to limit damage in the event of a "drought" crisis, even though weather warnings and alerts are being developed and the number of tools for forecasting the impact of climatic phenomena is increasing. In order to fill this gap, BRGM and its partners have proposed an innovative approach to RGA risk management through the development of a specific tool, called ViSéGéo (geotechnical drought vigilance), to take better account of geotechnical drought.
The results
ViSéGéo is an integrated risk management solution designed to improve the prevention of the risk of clay soil shrinkage and swelling, the financial impact of which is very high for France as a whole. Developed as part of a public-private collaborative research project and conducted jointly by BRGM, Prédict and Géosec, the project is being supported by the Occitanie-Pyrénées-Méditerranée Region and Europe (ERDF), under the READY'NOV call for projects, as well as by the French Ministry of Ecological Transition.
The aim of the project was to offer real-time monitoring of ground saturation conditions and the criticality of potential differential ground movements according to the nature of the geological formations in question. Based on these analyses, operational responses have been proposed, graduated according to the scale of the crisis observed/expected, and aimed at citizens who might be affected.
The scientific and technical content of the project has enabled the development of:
- Spatio-temporal characterisation for ranking the severity of RGA phenomena,
- methods of transferring information to the end users of the service (work carried out by Prédict),
- operational recommendations to limit/reduce the impact of the phenomena (work carried out in partnership with Géosec).
The flagship result of this project is the real-time mapping of the RGA hazard using GPS-tagged data on the geotechnical characteristics of ground and GPS and time tagged data on soil moisture (derived from Soil Water Index (SWI) data from Météo-France).
The solution developed is based on:
- a parametric study of the climatic, geological and geotechnical factors influencing the occurrence of phenomena, based on a statistical analysis at the regional level and on feedback since 1989;
- the development of specific processing algorithms to produce dynamic maps of the geotechnical drought hazard and the definition of thresholds;
- the development of a catalogue of operational measures to reduce hazards and/or the vulnerability of exposed infrastructures;
- implementation of a pilot model for the integrated solution.
A demonstrator for the Occitanie region, deployed by Prédict as part of its hydro-meteorological monitoring and warning activities, has been set up, with a view to applying it in other regions.
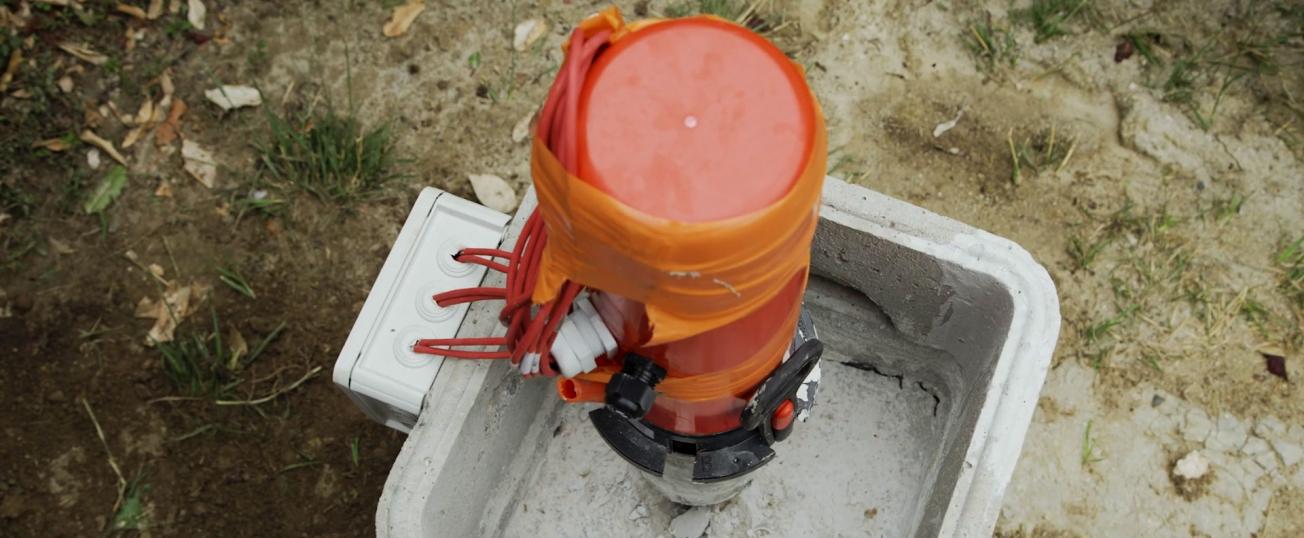
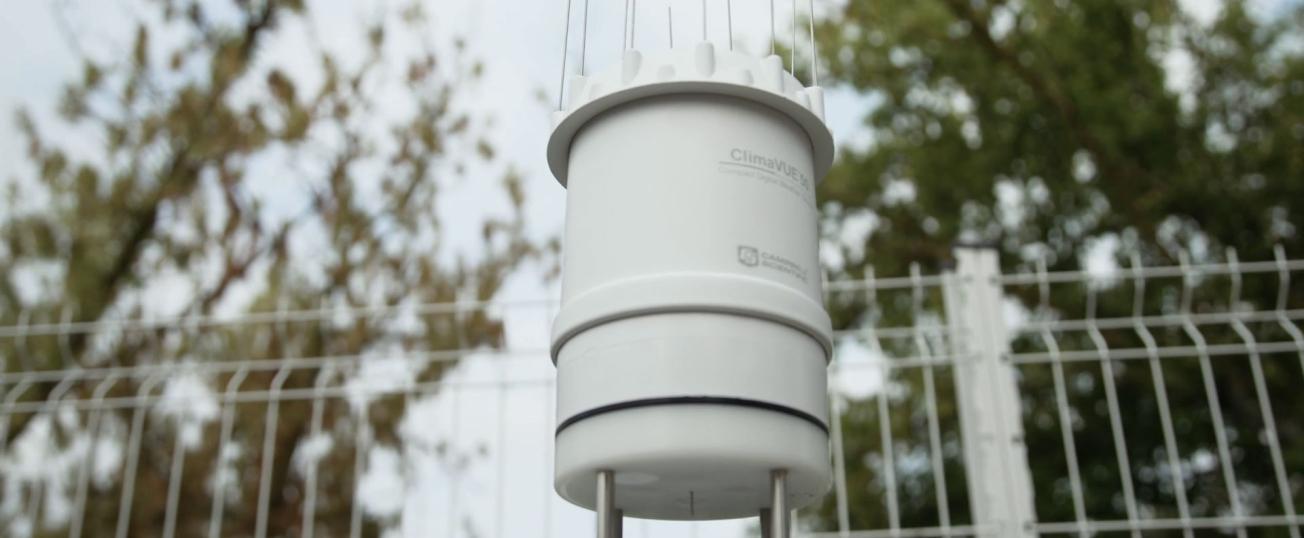
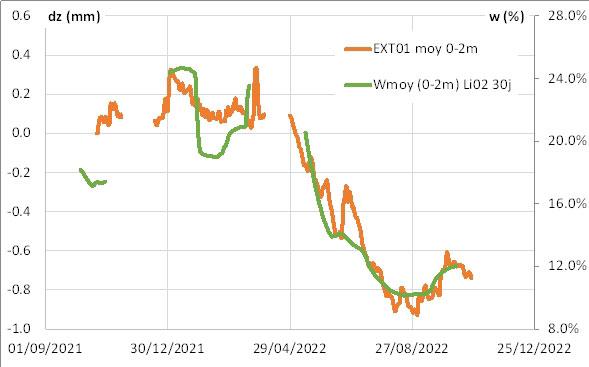
Concomitantly with this regional approach, instrumentation at two sites, in the communes of Labège and Cornebarrieu (Haute-Garonne), is providing valuable information on the development of geotechnical drought over time and at depth on a local scale. Soil moisture content and ground-deformation monitoring systems can be used to assess the relative influence of predisposing and triggering parameters (such as variations in soil moisture) on subsurface deformation. Geosec has also carried out tests on sites where resin has been injected, to quantify the effectiveness of the proposed treatments.
Using the results
The project's developments will support government departments in defining their policies for managing the risk of clay shrinkage and swelling. The results are intended in particular for:
- individuals that might be affected;
- risk-management contracting authorities (local authorities and government departments);
- insurance companies and major financial backers of financial coverage policies in the event of claims.